Hot oils and heat transfer fluids.
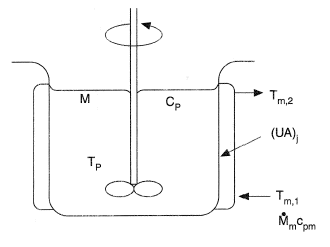
Jacketed vessel heat transfer coefficient.
This is to ensure that as little steam as possible condenses on the outer jacket wall and that the heat is transferred inwards to the vessel.
John pietranski pe created date.
The result is low allowable stress values for the inner vessel material.
Chemical engineering calculations to assist process plant operation and maintenance engineers.
The study of various methods of heat transfer in jacketed agitated vessels and the impact of altering different.
The recommended overall heat transfer coefficients will apply to typical conditions and installations.
A jacket is a cavity external to the vessel that permits the uniform exchange of heat between the fluid circulating in it and the walls of the vessel.
Therefore both half pipe jackets and dimple jackets can provide good solutions.
In this paper the heat transfer in polymer reactors has been investigated.
External jacket on the vessel or by internal coils.
Jacketed vessels may also be lagged or may contain an internal air space surrounding the jacket.
Where a jacket or coils cannot provide the surface area required a recirculation loop with an external heat exchanger may be used.
Heat transfer in agitated vessels is carried through heat exchange surfaces like jackets helical coils spiral coils and vertical tubular baffles the surfaces of heat exchange are designed as a function of the area necessary to carry the heating or cooling based on the overall heat transfer coefficient which is a function of the dimensionless groups.
Although pressures are usually low when using oils or heat transfer fluids the temperatures are usually high.
Jacketed vessel heat transfer calculation estimates overall heat transfer coefficient for a vessel with an agitator along with heating cooling medium flowing in jacket spiral jacket or half pipe coil.