You may use the designer for in situ probe design review your sequences save them to your cart and proceed to online checkout with just a few clicks you can also share your cart with your purchasing.
In situ hybridization probe design tool.
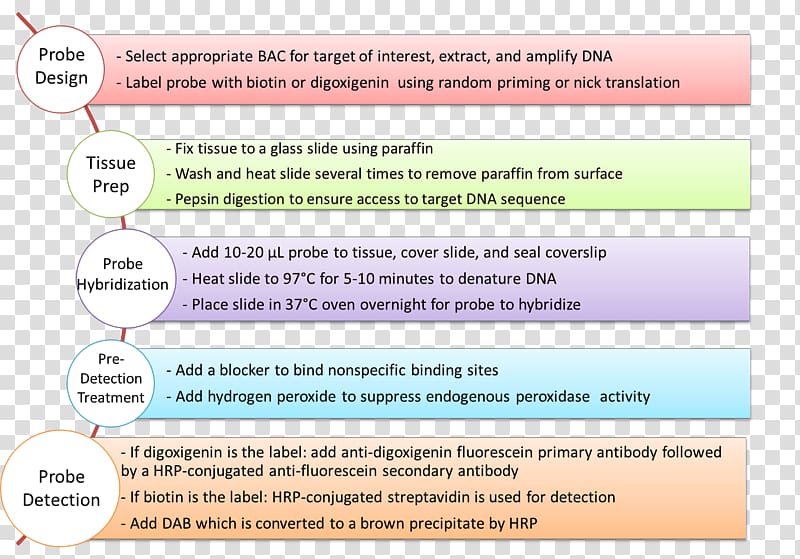
Thus probe design represents the first mandatory step for approaching nucleic acid in situ hybridization.
In situ hybridization of genes and mrna is most often based on polynucleotide probes.
This labeled rna or dna probe can then be detected by using an antibody to detect the label on the probe.
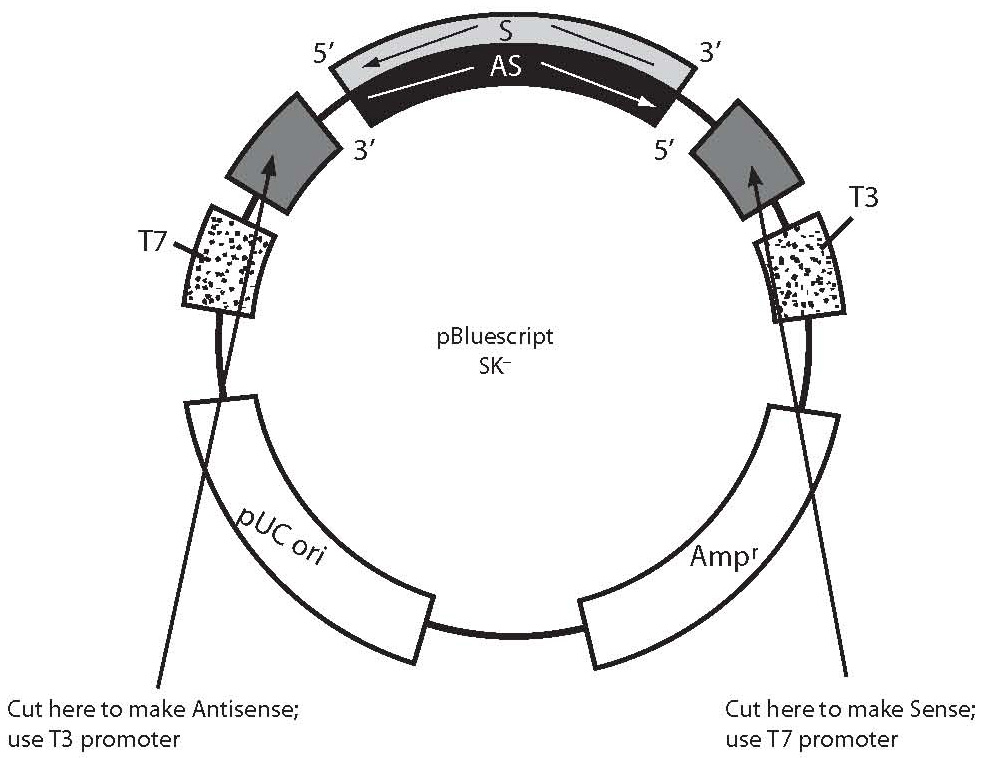
Despite the advances in dna technologies that now allow reliable and fast synthesis of oligonucleotides with several custom modifications comparatively little progress has been made in computational tools for accurate fish probes.
In situ hybridization indicates the localization of gene expression in their cellular environment.
Fish enables researchers to visualize the subcellular distribution of rna and dna molecules in individual cells.
Nucleic acid hybridization is an extensively adopted principle in biomedical research.
A labeled rna or dna probe can be used to hybridize to a known target mrna or dna sequence within a sample.
The recent development of fish methods employing probes composed of synthetic dna oligonucleotides oligos allows researchers to tightly control aspects of probe design such as binding energy and genomic specificity.
Several methods have been derived based on this principle to detect targets using sequence specific probes e g northern blot southern blot and in situ hybridization the lab protocol for probe hybridization is further optimized and miniaturized into microarray format to detect transcriptional activity.
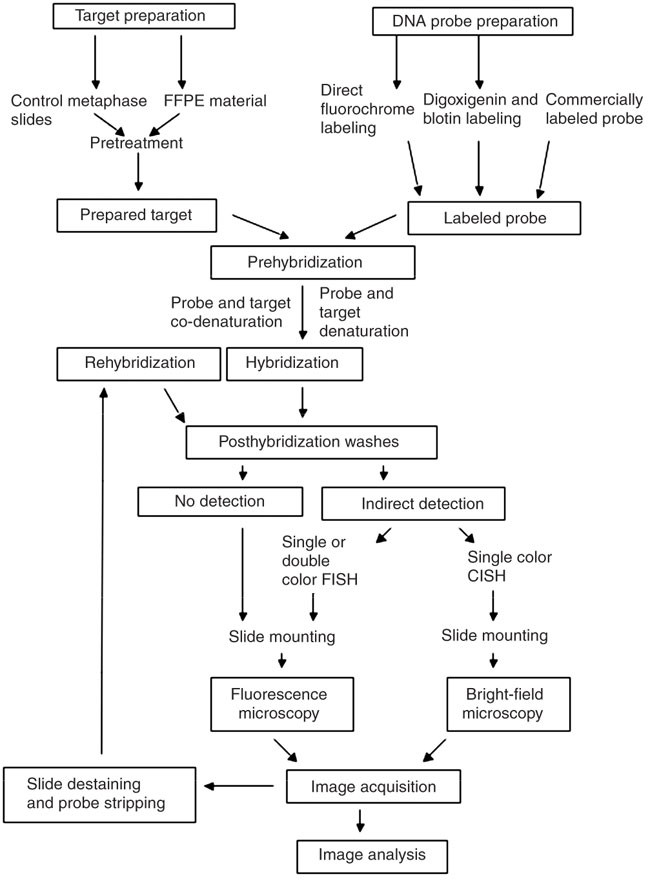
In situ hybridization ish is a technique that allows for precise localization of a specific segment of nucleic acid within a histologic section.
Global industry trends share size growth opportunity and forecast 2020 2025 report has been.
Fluorescence in situ hybridization fish is a molecular cytogenetic technique that uses fluorescent probes that bind to only those parts of a nucleic acid sequence with a high degree of sequence complementarity it was developed by biomedical researchers in the early 1980s to detect and localize the presence or absence of specific dna sequences on chromosomes.
21 2020 prnewswire the fluorescent in situ hybridization fish probe market.
Although oligo fish probes are central to many recently developed.
Modifications in probe design allows for a new barcoding system via sequence by hybridization chemistry for improved spatial detection of rna transcripts.