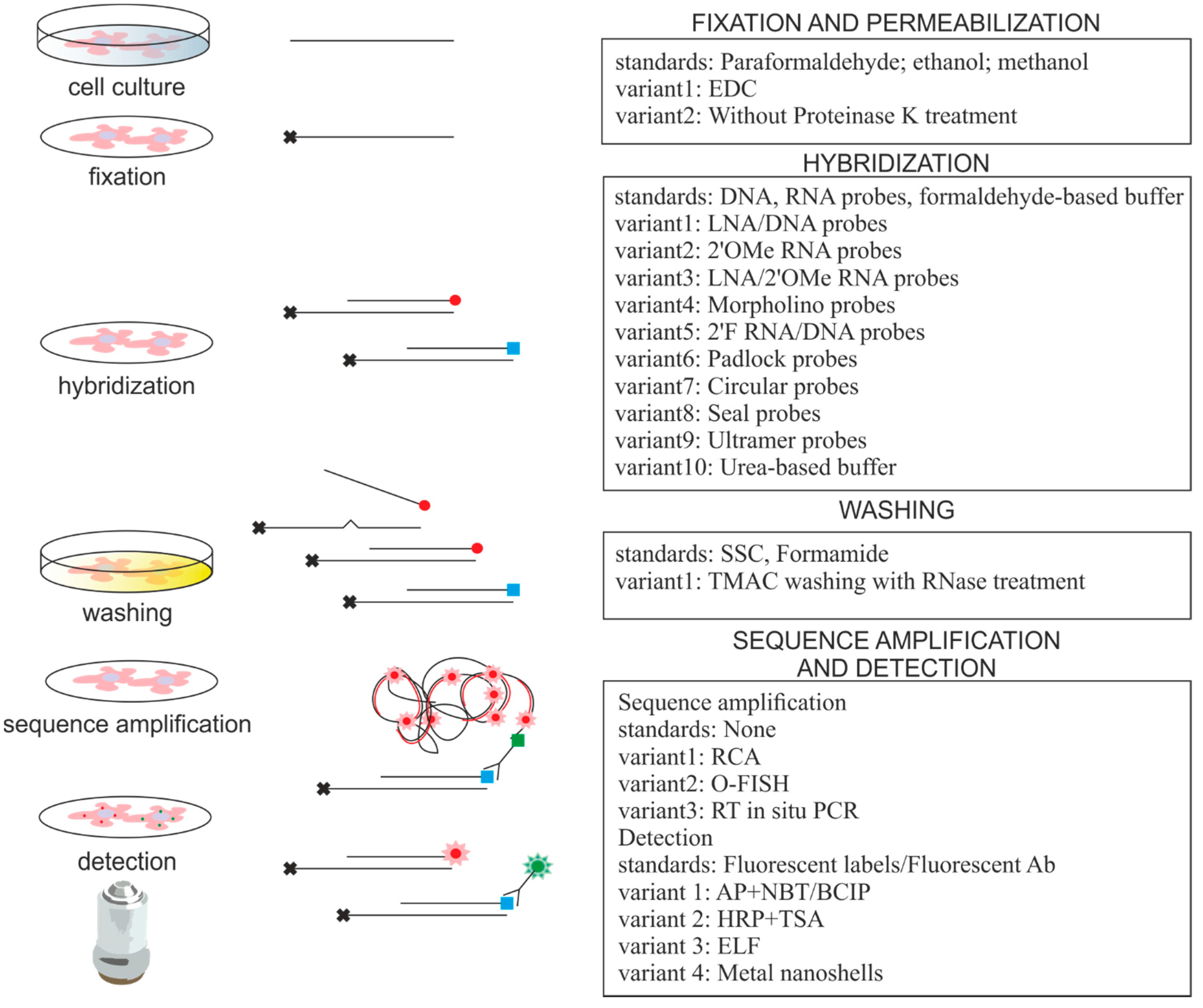
Oligonucleotide libraries with probes of 150 bp length can be synthesized in vitro enzymatically amplified and labeled and then used as in situ hybridization probes 14.
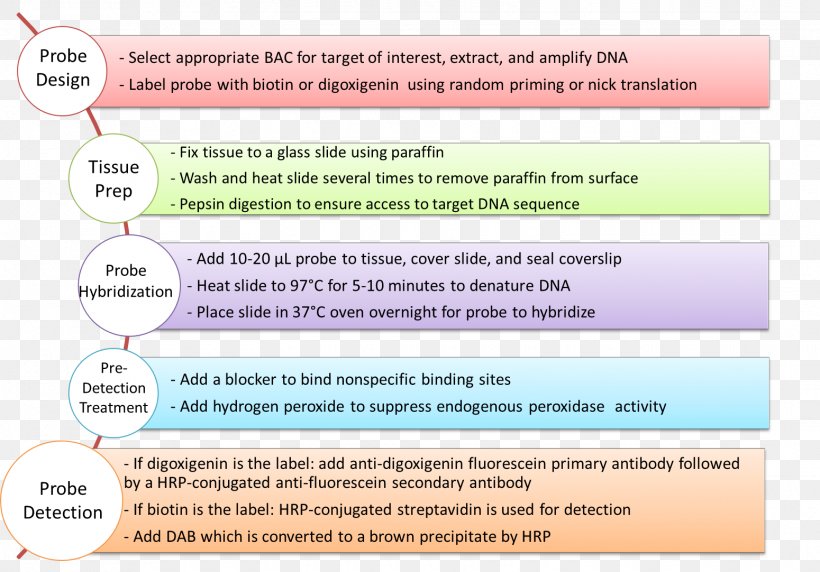
In situ hybridization dna probe design.
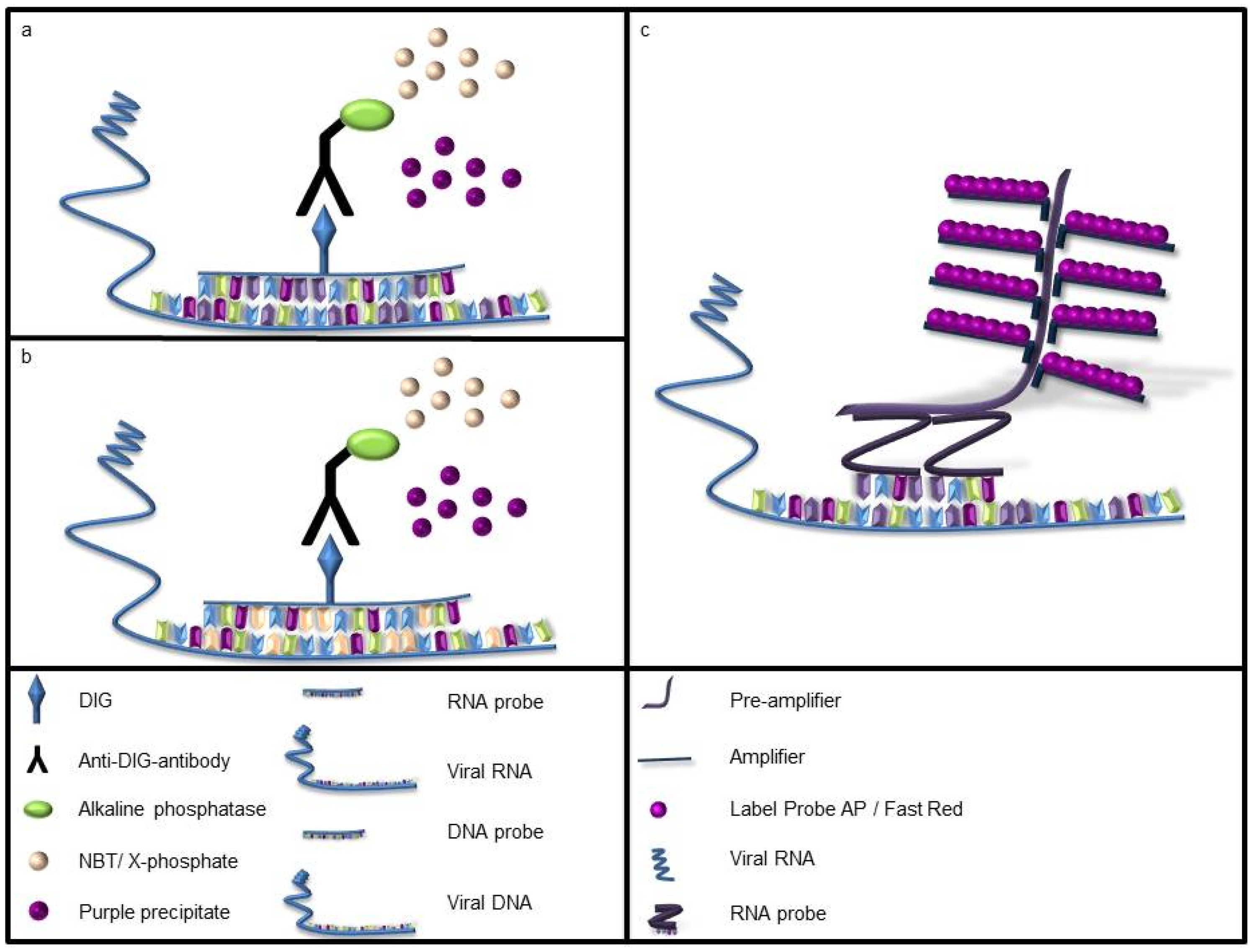
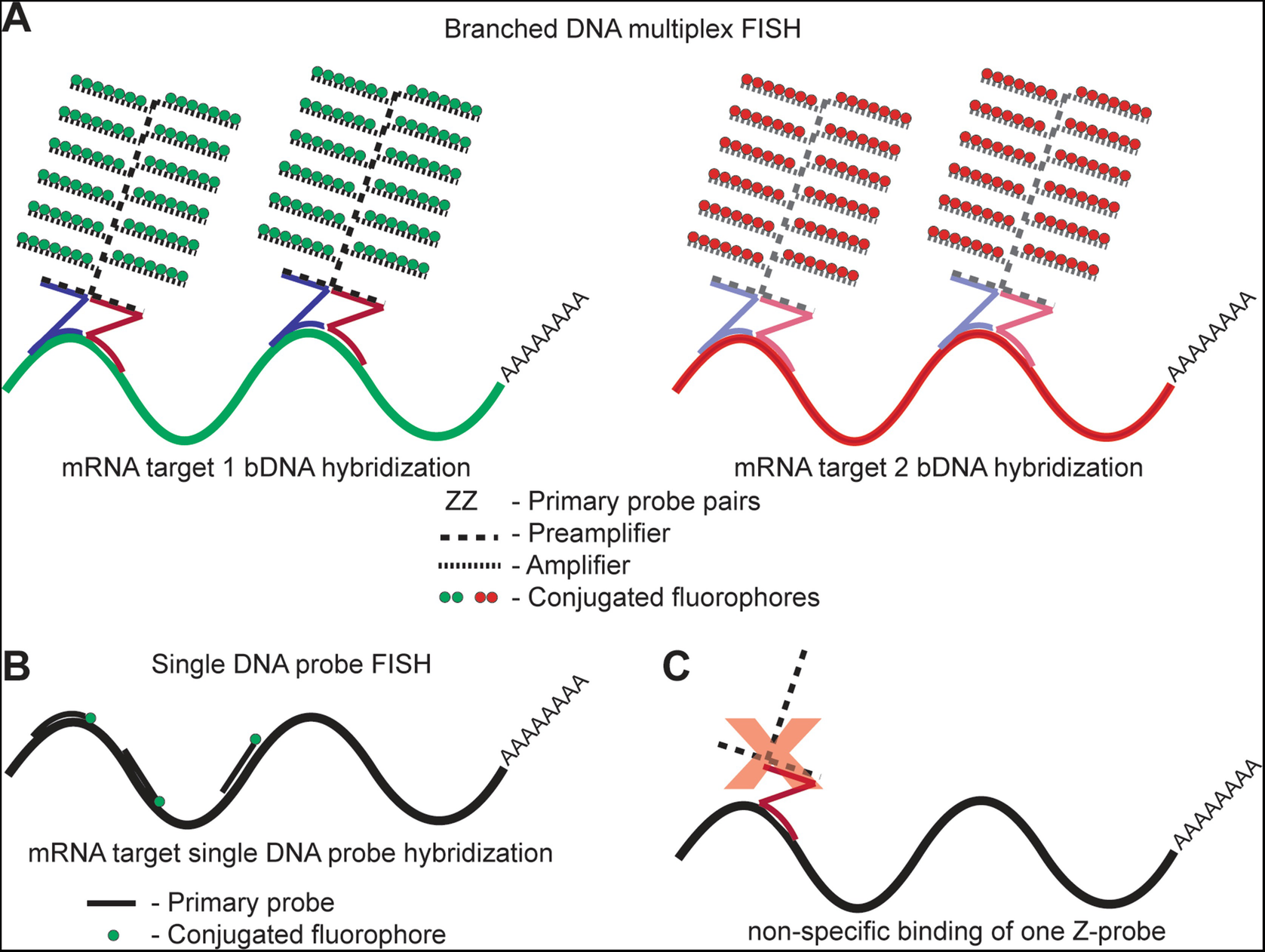
A labeled rna or dna probe can be used to hybridize to a known target mrna or dna sequence within a sample.
Additional recent advances within dna oligo printing have opened new possibilities for the design of in situ hybridization probes.
This labeled rna or dna probe can then be detected by using an antibody to detect the label on the probe.
However the specificity of polynucleotide probes has not been thoroughly investigated and a rational probe design concept was still missing because the well established concept for oligonucleotide probe design cannot be transferred to polynucleotides.
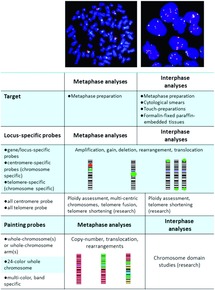
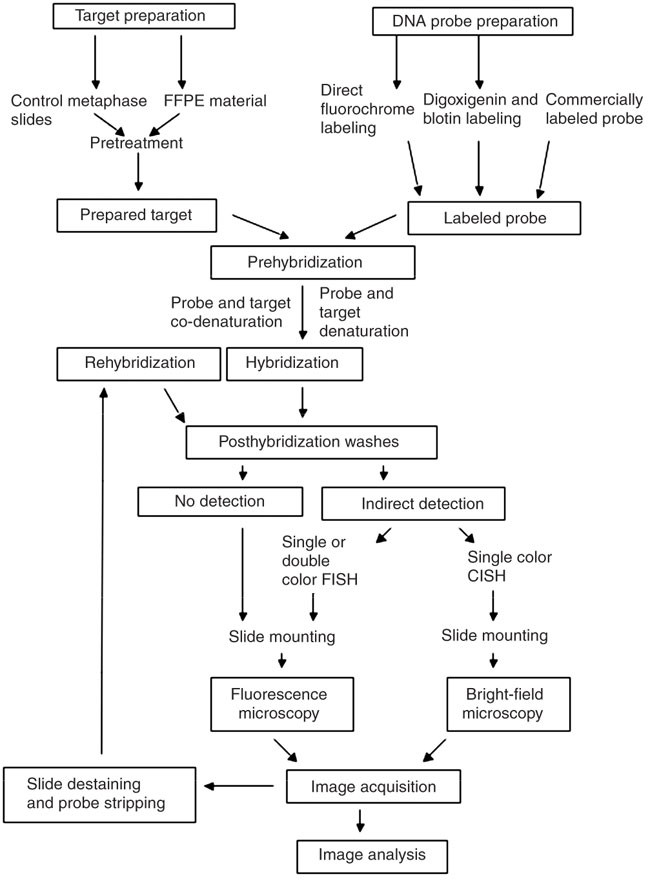
2 in situ hybridization protocol introduction in situ hybridization identifies where in the cellular environment a gene is expressed.
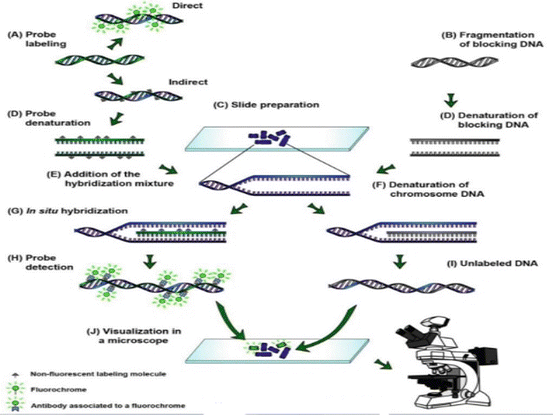
In situ hybridization ish is a technique that allows for precise localization of a specific segment of nucleic acid within a histologic section.
The underlying basis of ish is that nucleic acids if preserved adequately within a histologic specimen can be detected through the application of a complementary strand of nucleic acid to which a.
In situ hybridization ish is a type of hybridization that uses a labeled complementary dna rna or modified nucleic acids strand i e probe to localize a specific dna or rna sequence in a portion or section of tissue or if the tissue is small enough e g plant seeds drosophila embryos in the entire tissue whole mount ish in cells and in circulating tumor cells ctcs.
In situ hybridization indicates the localization of gene expression in their cellular environment.